What kind of signals did the Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer and other big pharmaceutical companies have signed up with the medical AI company?
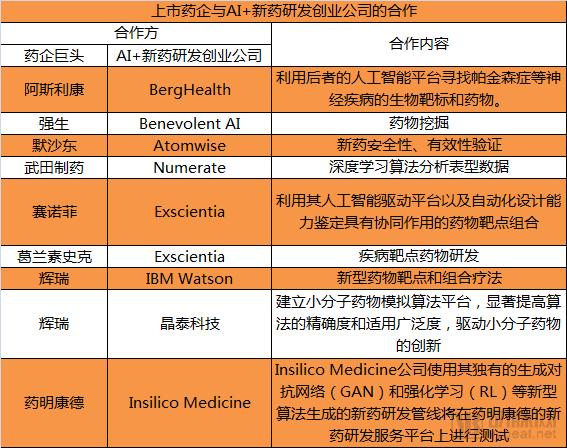
Looking at the recent medical AI-related industry forums, everyone has added commercialization to the content setting. When medical AI products are gradually polished and tried in hospitals, commercialization has become the most concerned thing for capital, enterprises and other related practitioners. However, since most of the new-generation medical AI products are positioning auxiliary diagnostic products, these products have not yet been approved by the Food and Drug Administration, so the commercialization of such products is only at the trial stage, and it cannot be widely promoted and landed. The application of AI in the field of new drug research and development is mainly in the aspects of new drug discovery, safety and effectiveness testing. The threshold of these applications is mainly technical, not regulatory. The long development cycle and high cost of new drugs have become a major pain point in the industry. Therefore, once the products discovered by AI+ new drugs are mature, it is not very difficult to land. Arterial Network recently learned that the pharmaceutical giant has begun to choose to accelerate drug development with AI technology in the last two years, and chose to cooperate with the medical AI startup to accelerate the advancement of this matter. For example, AstraZeneca and BergHealth, Johnson & Johnson and Benevolent AI, Merck and Atomwise, Takeda Pharmaceutical and Numerate, Sanofi and GlaxoSmithKline and Exscientia, Pfizer and IBM Watson, Pfizer and Jingtai Technology have all formed partnerships. . The Arterial Network conducted an inventory of these collaborations to understand their collaborative content. Jingtai Technology and Pfizer In May 2018, Jingtai Technology, an AI pharmaceutical research and development company with algorithm-driven innovation, announced that it has signed a strategic R&D cooperation with Pfizer, integrating quantum physics and artificial intelligence, and establishing a platform for small molecule drug simulation algorithms, which significantly improves the accuracy and application of the algorithm. Degree, driving innovation in small molecule drugs. Drug simulation is widely used in drug discovery and design, allowing scientists to study and predict the biological, pharmaceutical properties and reactions of drugs from the atomic layer. In this cooperation, Jingtai Technology will take advantage of its quantum mechanics, artificial intelligence, and cloud-based high-performance scientific computing to improve and break through existing drug simulation technologies, allowing this platform to cover a wider range of chemical spaces. And generate a more accurate molecular model of the drug. On this basis, the platform will also achieve accurate predictions of several key properties of the drug, further empowering important aspects of drug discovery and development. The establishment of this strategic R&D cooperation benefited from the good cooperation foundation between Jingtai Technology and Pfizer. Its drug crystal form prediction technology is favored by Pfizer, and this drug simulation algorithm platform will further enhance the technical strength of both sides in the calculation of assisted drug design and drug solid phase screening. In order to promote the technical exchanges between industry, academia and research, this research and development will also open a part of the molecular mechanics parameters based on the open database for the academic community to promote and support the continuous progress and innovation in related fields. WuXi PharmaTech and Insilico Medicine On June 11, 2018, Insilico Medicine, a new generation of artificial intelligence company in the United States, announced that it has signed a cooperation agreement with China's pharmaceutical R&D service industry leader WuXi PharmaTech. Under the agreement, Insilico Medicine will use its unique new drug discovery pipeline to generate new algorithms for combating networks and reinforcement learning to be tested on WuXi PharmaTech's new drug development service platform. The two companies have developed a series of milestones designed to develop ideal preclinical drug candidates using next-generation artificial intelligence techniques for new and challenging biological targets, such as unknown crystal structures or ligand targets. Since 2016, Insilico Medicine has published several research papers showing the ability to generate new drug molecules with the desired properties using GAN and RL artificial intelligence techniques, and screening some of the most promising pipelines through preliminary experimental verification. molecular. The collaboration with WuXi PharmaTech will enable the company to quickly further validate the drug candidate molecules it discovers and simultaneously generate valuable data to advance the development of its artificial intelligence technology. Berg Health and AstraZeneca In 2017, AstraZeneca and the Massachusetts startup BERG established a partnership to use the latter's artificial intelligence platform to find biological targets and drugs for neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease. How to use artificial intelligence? BERG CEO Niven R. Narain said that the first thing is to "return to biology." Tissue samples were taken from healthy individuals and patients, subjected to various molecular analyses, combined with clinical data, and then identified by BERG's artificial intelligence platform. Narayin said that in the data analysis, BERG will avoid the "open database." He said: "We use the Bayesian method, not the neural network. Instead of putting a batch of data into the model and then come out Some sort of correlation is so simple. There is no presupposed assumption at the beginning, but all the data is entered into the system, allowing the data to generate the hypothesis itself." As early as October 2016, Berg Health and the US Department of Defense announced a partnership to use artificial intelligence technology to develop new drugs. In search of invasive breast cancer treatment options that respond to existing drugs, up to 250,000 samples will be screened for new biological indicators and biomarkers for early cancer. BenevolentAI and Johnson & Johnson In November 2016, BenevolentAI and Johnson & Johnson reached a cooperation, Johnson & Johnson transferred some of the small molecule compounds still in the test to BenevolentAI for new drug development. BenevolentAI's technology platform uses artificial intelligence technology to extract knowledge that drives drug discovery from these distracting amounts of information and to propose new verifiable hypotheses that accelerate drug discovery. This technology platform is called JACS (Judgment Augmented Cognition System). For more details: "BenevolentAI: The largest artificial intelligence + new drug research and development company in Europe, the two kinds of drugs are sold for 800 million US dollars" Merck and Atomwise In 2015, Merck worked with Atomwise in the United States, and its groundbreaking AtomNet technology platform is like a human medicinal chemist. It uses powerful deep learning algorithms and supercomputer tools to analyze millions of potential therapies every day to speed up drugs. R&D process. Mainly targeted at the effectiveness and safety of new drugs. In May 2018, Atomwise received $45 million in financing, and both Baidu Ventures and Tencent participated in the investment. Atomwise's groundbreaking software technology, AtomNet, uses powerful deep learning algorithms and super-calculations to analyze millions of molecules every day, like human chemists, to screen potential drugs. In the past two years, Atomwise has developed rapidly and has established partnerships with the top ten pharmaceutical companies in the United States, several biotechnology companies, and more than forty major research universities. At the same time, more than 50 research and development projects are underway. Atomwise has partnered with four large pharmaceutical companies, including Merck, and has close relationships with many other biotech companies, research institutions and universities. Takeda Pharmaceutical and Numerate In June 2017, Numerate officially signed a contract with Takeda Pharmaceutical to collaborate on the use of Numerate's artificial intelligence (AI) to find small molecule drugs for oncology, gastroenterology and central nervous system diseases. Numerate CEO Guido Lanza said they applied AI to chemical design at all stages. Numerate collaborated with Takeda Corporation of Tokyo to screen target molecules, design and optimize compounds, model drug absorption, distribution, metabolism and elimination, and toxicity, and provide Takeda with clinical trial candidates. The amount of the agreement and the royalties were not disclosed. In Japan, in addition to Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Fujifilm and Yanyeyi Pharmaceutical will use artificial intelligence (AI) to promote new drug development. About 50 companies, including IT companies such as Fujitsu and NEC, participate in the project. The Institute is working with the Institute of Physical Chemistry and Kyoto University to develop artificial medicinal intelligence to quickly find candidate substances that can be used to make new drugs. At present, the development of new drugs requires huge costs, and the success rate is only 20,000-30,000. The use of artificial intelligence will increase development efficiency and increase competitiveness in the development of intense global new drugs. A coalition of companies and research institutions will be launched soon. Not only in Japan, but also overseas IT companies and pharmaceutical companies are expected to participate. Strive to develop new drug development based on artificial intelligence with the goal of three years later. The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology will add 2.5 billion yen to the 2017 budget estimate request to support the project. The final total is expected to reach 10 billion yen. Sanofi and Exscientia In May 2017, according to the GEN website, Sanofi and Exscientia signed a cooperation and licensing transaction with a potential value of 250 million euros (about 276 million US dollars). The deal aims to develop bispecific small molecule drugs for metabolic diseases. Exscientia will use its artificial intelligence-driven platform (AI)-drivenplatform and automated design capabilities to identify synergistic drug target combinations, and then use its lead-finding platform to identify bispecific small molecule drugs for these targets. . Exscientia will be responsible for all compound designs and Sanofi offers chemical synthesis. In addition, Sanofi retains the option to license "related compounds" and will undertake future preclinical and clinical development. Exscientia will receive research funding for identifying “target pairs†and priority drug candidates and will be eligible for future non-clinical, clinical, and sales-related milestone payments. Exscientia's drug development "engine" is built on an AI platform. Companies can use the platform to design and evaluate new compounds, including potency, selectivity, and ADME. The company is using the platform to build partnerships to develop small molecule drugs for single targets and bispecific small molecule candidates for target combinations. In addition to this new transaction, in April 2016, Exscientia and Germany Evotec reached an agreement on the Immuno-Oncology. At the AACR annual meeting last month, the two sides published details of selective adenosine 2A receptor antagonists and bispecific small molecule drugs (targeting A2AR and CD73). The Exscientia partner Sanofi also has a partnership with Evotec. The two sides have reached a cooperation in 2015, including cooperation in the development of beta-based diabetes therapy. GlaxoSmithKline and Exscientia In July 2017, the large pharmaceutical company GlaxoSmithKline announced that it had reached a US$43 million deal with the British AI company Exscientia. Exscientia will use its artificial intelligence platform to assist GlaxoSmithKline in developing 10 drugs. Exscientia will receive a total of 33 million pounds, based on research and development results, at a contract value of $43 million. Exscientia CEO Hopkins said the company's AI system can complete new drug candidates in just a quarter of the time and cost of traditional methods. Exscientia also signed an agreement with Sanofi in May. Other large pharmaceutical companies, including Merck, Johnson & Johnson and Sanofi-Aventis, are also developing the potential of artificial intelligence to help the drug development process become smoother. These manufacturers hope to use modern supercomputers and machine learning systems to predict how the various molecules in the drug will behave and how likely they are to succeed, so that they don't have to spend time and money on unnecessary tests. IBM Watson and Pfizer IBM Watson and Pfizer have reached a new agreement that will use the former's supercomputing power for cancer drug development. Pfizer will use Watson for Drug Discovery's machine learning, natural language processing and other cognitive reasoning capabilities for new drug identification, combination therapy and patient selection strategies in immuno-oncology. Watson for DrugDiscovery is a new cloud platform designed to help life scientists discover new drug targets and indications for alternative drugs. According to Pfizer, many researchers believe that the future of immuno-oncology lies in the combination of unique tumor characteristics, which will change the cancer treatment paradigm and allow more cancer patients to be treated. And immuno-oncology is a cancer treatment that uses the body's immune system to help fight cancer. The amount of these cooperation is more than 10 million US dollars In June 2017, Arterial Network had counted 16 companies engaged in the research and development of AI+ new drugs. These companies now have more than 8 companies that have business cooperation with pharmaceutical companies. From the scale of known cooperation, the amount is in the thousand. Ten thousand dollars and hundreds of millions of dollars. For example, GlaxoSmithKline and Exscientia deal $43 million. BenevolentAI teamed up with a US pharmaceutical company to sell two new Alzheimer's drugs under development to the US company, which are in the evaluation phase of the candidate compound. The deal was worth $800 million and the BenevolentAI received a $400 million advance payment. From the current situation, the medical AI company's revenue for domestic positioning-assisted diagnosis is still research funding, technical services or other business, and it will take time to achieve large-scale revenue. Surprisingly, the domestic companies engaged in the research and development of AI+ new drugs are mainly Jingtai Technology and Bingzhou Stone Bio. There are several domestic medical AI companies that already have hundreds of researchers. Is it possible to consider the layout of new drug research and development, worthy of the founding team? Thinking. The AI ​​era may be a good opportunity for the rise of new pharmaceutical companies According to the revenue data of foreign pharmaceutical companies' 2017 financial report, the top ten pharmaceutical companies are Pfizer, Novartis, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Merck, Johnson & Johnson, Sanofi, Aibowei, Lilly, Amgen. The top ten of R&D investment by global pharmaceutical companies The top ten list of pharmaceutical companies has changed little in recent years. Because their R&D investment will support future revenue. Without new technologies and changes brought about by new technologies, this pattern will not be easily broken. In Japan, for example, the National Research and Development Corporation, the Institute of Basic Health and Nutrition, plans to use the existing artificial intelligence to find new drug candidates from 2017. According to the arterial network, the newly developed artificial intelligence for the development of new drugs can improve the accuracy by learning various data, and can also track the causes of the effects of new drug candidate substances, which is helpful for promoting clinical applications. Takeda, Japan's largest pharmaceutical company, ranks 17th in the global pharmaceutical industry (Japan's Takeda Pharmaceuticals, after acquiring Irish pharmaceutical giant Shirei Pharmaceuticals, ranks in the top 10), and is inferior in size to pharmaceutical giants such as Pfizer and Swiss Novartis. Development costs are only less than half of the major pharmaceutical companies such as Pfizer. Without artificial intelligence to improve R&D efficiency, Japanese pharmaceutical companies will not be able to win in global competition. In the recent “China Innovative Medicine Decade Outlook†released by CICC, it is mentioned that by 2030, China’s contribution to global pharmaceutical innovation will increase from the current 2% to the “new active ingredients†developed. 12%, entering the second echelon of the world. The proportion of Chinese companies in global pharmaceutical R&D will increase from the current 5% to 20%, surpassing the UK and ranking second. China will produce 1-2 new First-in-Class drugs each year. In the past decade, there have been 3-5 blockbusters with global sales exceeding $1 billion. 20% of innovative drug sales will come from overseas markets. The huge application prospects of artificial intelligence in drug development will shorten the time of drug development and reduce costs, which provides a possibility for innovative pharmaceutical companies to break the existing pattern. However, domestic pharmaceutical companies should also note that the layout of international traditional pharmaceutical giants in the field of medical AI has been very deep, and domestic should also consider using AI to speed up drug development and avoid missing this round of technology dividends. It is worth mentioning that medical AI will make Chinese medicine more reliable: many people do not trust Chinese medicine, because most Chinese medicines are marked with specific molecular pharmacological mechanisms and side effects. If AI pharmaceutical technology is applied to traditional Chinese medicine research, it will be a milestone in development. Through deep learning, AI constructs a neural network, absorbs known organic chemical reactions, contacts molecules in drugs, and finally analyzes pharmacological mechanisms. It seems that AI-assisted new drug development will become a good opportunity for the emergence of new pharmaceutical companies.
Organic erythritol is produced through multiple hydrolysis and fermentation of corn starch. It is a natural sweetener. Erythritol is usually white particles or powder.
The sweetness of erythritol is only 60%-70% of that of sucrose. It has a refreshing taste, pure taste, and no bitterness. It can be used in combination with high-power sweeteners to suppress the bad flavor of high-power sweeteners.
Erythritol is different from traditional sugar. It is very stable to acid and heat and has high acid and alkali resistance. It will not decompose and change below 200 degrees, and will not change color due to the Maillard reaction. Erythritol has an endothermic effect when dissolved in water, and the heat of dissolution is only 97.4KJ/KG, which is higher than glucose and sorbitol, and has a cooling sensation when eaten.
It does not participate in sugar metabolism and blood sugar changes, so it is suitable for diabetics. It does not cause fermentation in the colon and can avoid gastrointestinal discomfort. It does not cause tooth decay.
Organic erythritol is the most reliable choice in many fields, such as beverages, candies, baked goods, dietary sweeteners, and functional foods. We provide pure organic erythritol and a mixture of erythritol and any other natural sweeteners!
Our organic corn farm is located in Heilongjiang Province, where the soil is fertile, especially suitable for growing corn. Our organic erythritol is produced in strict accordance with the organic standards of the European Union and the United States Department of Agriculture.
Organic Erythritol,Erythritol Sweetener Organic,Organic Erythritol Powder,Organic Erythritol Sweetener Organicway (xi'an) Food Ingredients Inc. , https://www.organicwayince.com