Talking about Drought and Drought Resistance Technology of Vegetable Cultivation
Now it's spring, and summer is not far away. How do you manage vegetable cultivation in the hot summer? The following are some of the drought-proof and drought-resistant engineering techniques, agronomic management and pest control measures in vegetable cultivation in the drought season. 1 Engineering and technical measures The drought prevention and drought resistance engineering measures mainly aim to solve the problems of water storage, water source maintenance, water saving irrigation, and reduction of runoff, leakage and evaporation losses in water-deficient vegetable producing areas and dry seasons. 1.1 Micro-drip irrigation technology Micro-drip irrigation is a method of irrigation by spraying or dripping water onto plants and soil surfaces at a small flow rate through a low-pressure piping system. This kind of irrigation technology can draw water close to the water, meet the water requirement of crops with a small amount of water supply, and the irrigation time is not limited. The water supply can be based on the water demand of the crop, the water consumption is small, the leakage loss is small, and the pipeline engineering is easy to operate after installation. Easy to manage, save labor and effort. The application results show that in the winter, the cultivation of zucchini in winter is 77.7m3 per 667m2 of drip irrigation, 97.1m3 of water saving compared with Mingshui, and 55% of water saving; spring tomato is watered for 8 days, drip irrigation is 99.9m3 per 667m2, 50% water saving than Mingshui irrigation. . It is suitable for long-season vegetable cultivation in flat land, facilities, mountains and other places near water. 1.2 Film mulching technology The mulching film covering technology covers the mulch film planting vegetables, and uses the effect of mulching film to moisturize, collect rain and drought, protect fertilizer and weed, and prevent insects and disease, improve soil water retention rate and prolong crop drought resistance. Generally, for vegetables with high ground temperature requirements, shallow roots and short growth period, the yield increase can reach 30% to 50% on average. Combined with membrane or sub-membrane drip irrigation technology can play a better water retention and drought resistance. The mulching film covering technology is easy to operate and low in cost, and is generally applicable to dryland planting. 1.3 Rainwater harvesting technology The rainwater harvesting irrigation technology is to build a rainwater harvesting facility such as a waterlogging in the irrigated agricultural area according to the natural slope, runoff, etc., to store water, collect rainwater and surface runoff during the rainy season, and to supplement the irrigation water source during the dry and dry seasons. The construction of water collecting facilities can ensure timely crop planting and supplement irrigation with precipitation to meet the water needed for crop growth and development, so that the agriculture in the arid region can be changed from passive drought resistance to active drought resistance, increasing natural precipitation utilization rate and achieving average water saving. More than 30%. It is generally suitable for mountainous hills where alpine vegetables are grown, such as insufficient water sources and difficult water diversion areas. 1.4 “Small Earth Dragon†irrigation technology The "small earth dragon" irrigation technology uses a micro-spray belt to kill the end of the micro-spray belt outlet, open a certain number of small holes in the plastic pipe, and use a mobile water pump to supply water to form water from the micro-spray belt. Strip sprinkler technology. Generally, the micro-spray belt has a diameter of about 60 mm, and the length of the perforated pipe laid in the field is about 100 m. The spray width is generally 4 to 5 m, which can be connected to a water supply pipe of 100 to 200 m. Usually, a 3.2 kW submersible pump is used. Water supply (pump power may be increased or decreased due to different depths and lifts, other water sources may be used). The irrigation time may be about 466.7 m2 and the irrigation time is about 45 min. After the irrigation is completed, the micro-spray belt is manually moved to another place for sprinkling. The average sprinkler irrigation is less than 1 h on 667 m2. With such a set of "small earth dragons", two laborers can irrigate about 4666.7 m2 a day. The technology is low in cost, simple in operation, can be taken from different places, mobile irrigation, and convenient to carry, and is suitable for individual farmers in dry areas with relatively flat terrain, water intake in different places, and low cost input. 2 Agronomic management measures 2.1 Seedling transplanting When the water source is insufficient, large area, etc. will delay the suitable sowing period, the seedling transplanting method can be used. Seedling seedlings can be used to seedling seedlings or seedlings can be planted on the ground. Before planting, watering the bottom of the feet, adding farmyard manure, no watering in the later stage of planting. . The transplanting time can be flexibly grasped. Generally, when 6 to 8 leaves are used, it can be transplanted in batches or transplanted after rain. 2.2 Drought-resistant seedlings After transplanting, focus on seedlings and try to keep the soil moist. During continuous high temperature and drought, watering can be watered for 3 to 5 days. It is better to water or ditch in the morning and evening, and drain the water to the ditch and drain the remaining water. Conditional use of micro-spray drip irrigation, micro-storage micro-irrigation and other drought-resistant and water-saving measures, saving labor and quality, irrigation quality. 2.3 shading and cooling The shading net is used to cover the protection measures of the top of the greenhouse to block the strong light and lower the temperature to prevent high temperature burning and reduce the adverse effects. Planting kneading can cover weeds, straw, used sunshade nets, etc., reducing soil moisture evaporation. 2.4 Water Management Dryland vegetables should be watered in the morning or evening to avoid high temperature irrigation. The amount of water and the time of irrigation can be judged by combining the determination or observation of soil water content. Generally, when the relative water content of the soil is less than 60% or the soil of the hand-squeezed soil is loose and does not form a cluster, it indicates that the soil is dry and needs timely irrigation. The amount of irrigation is just enough to penetrate the roots of the plants, and there is no runoff on the surface. Aquatic vegetables can be poured into deep water to cool down in time to protect them from high temperatures. The conditional place adopts live water irrigation or daily irrigation night drainage, which not only has the effect of cooling, but also effectively increases the humidity of the field air, improves the microclimate, promotes the robust growth of the root system, and enhances the ability of the plant to resist high temperature. 2.5 Fertilization techniques According to the principle of thin fertilizer application, every 7 days or so, in the morning or evening, apply biogas slurry fertilizer, rare manure, 0.3% urea or other foliar fertilizer, and conditionally use drip irrigation to improve the drought resistance and resistance of crops. Plant growth. For vegetables that delay the replanting in autumn, increase the quick-acting fertilizer and reduce the slow-acting fertilizer; increase the base fertilizer and seed fertilizer, reduce the topdressing, and realize the advancement of fertilizer; reduce the proportion of nitrogen fertilizer, especially the nitrogen fertilizer in the middle and late stages. Cautious application, increase the proportion of phosphorus and potassium fertilizer, promote crop growth and improve its resistance to stress; due to the shallow and weak roots of late-sown crops, the depth of fertilization should be increased to approach the roots of crops for easy absorption. 3 pest control measures High temperature and drought are easy to induce pests and diseases. Beet armyworm, Spodoptera litura, and melon are more serious. Field management should strengthen pest control. Spraying pesticides in high temperature should also pay attention to prevent crop phytotoxicity and personnel safety. It is recommended to promote the application of pest control. Non-pesticide control measures such as net cover, insecticidal lamps, insect attractants, swatches, and high-efficiency and low-toxic pesticides reduce the number and usage of pesticides and increase yield and quality. At the same time pay attention to the safety interval of pesticides. The above is the drought-proof and drought-resistant technology for vegetable cultivation. You can learn more from the farmers and see if it can be applied in the upcoming hot weather.
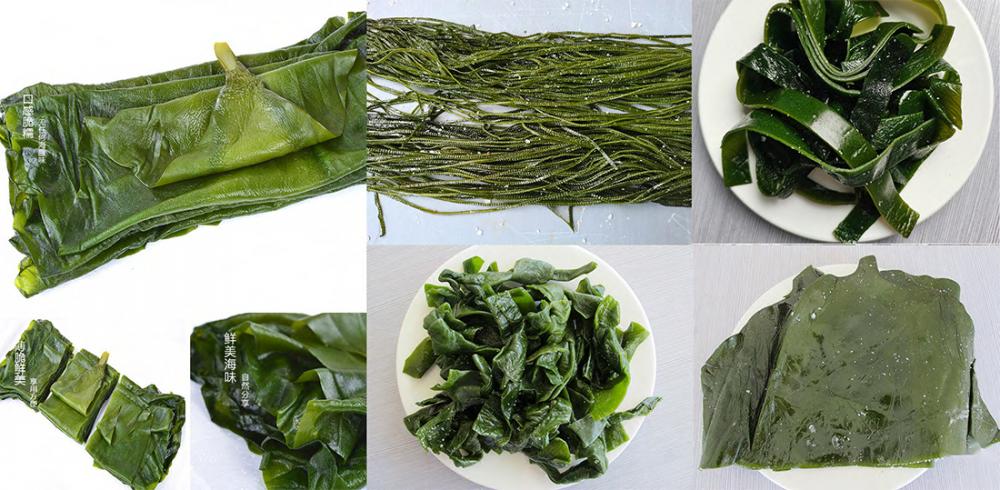
Salted Wakame Leaves
The original ecological kelp means that we pack the young kelp with saturated salt water directly after washing without any preservatives.Original ecological products are the favourite of housewives.
How to eat:
The difference between deep sea kelp and traditional ordinary kelp
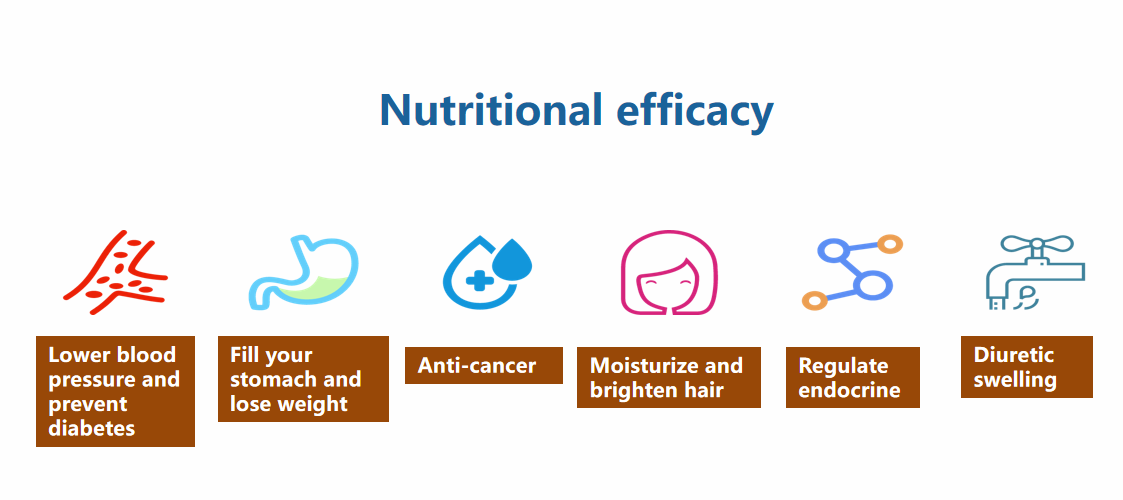
Nutrational Effects
Salted Wakame Leaves,Dried Wakame ,Wakame Sea Vegetable,Organic Wakame Seaweed Shandong Haizhibao Ocean Science and Technology Co.,Ltd. , https://www.haizhibaoseafood.com