Peanut yellow leaf more iron
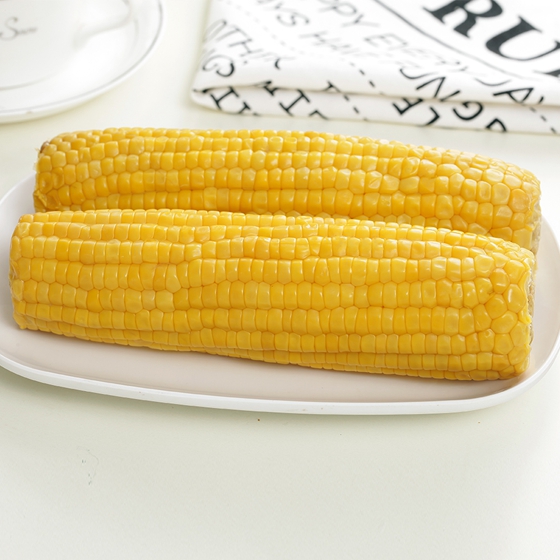
Wang Hu A: The reason is due to the lack of iron in peanuts. I. Symptoms: When peanuts are deficient in iron, they first appear as chlorosis of the upper young leaves, while the old leaves and veins of the lower part remain green; when the iron is severely deficient, the veins of the leaves lose their green and yellow, and the upper new leaves become white. Brown spots appear necrotic, dry and fall off. Compared with the chlorosis caused by nitrogen deficiency and zinc deficiency in peanuts, the outstanding performance of iron deficiency and chlorosis in peanuts is that the leaf size has no significant changes and the chlorotic chlorosis is significant. The lack of nitrogen caused by yellowing and chlorosis often leaves thinner, smaller plants, dwarf; zinc deficiency can cause large clusters of leaves, yellow and white small leaf spots. A medium-sized cob of corn provides more than 10% of our daily dietary fibre requirements.
Fibre is fermented by bacteria in the colon. Promising studies are underway to determine the health-promoting effects of fibre fermentation breakdown products, for example, short-chain fatty acids, which may help to maintain a healthy gut.
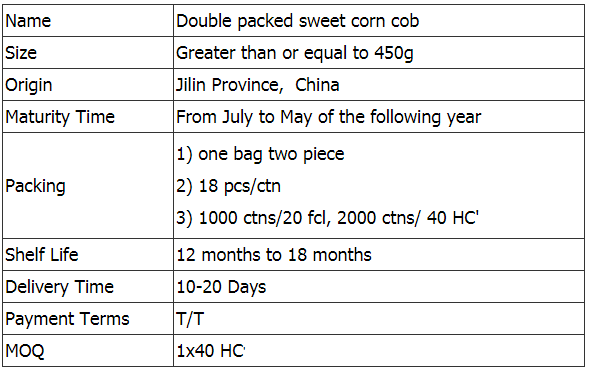
Yellow Sweet Corn,Double Packed Sweet Corn,Double Packed Sweet Corn Cob,Double Packed Yellow Sweet Corn Jilin Province Argricultural Sister-in-law Food Co., Ltd. , https://www.nongsaocorn.com
Second, the prevention and control methods: In the production of 0.1% to 0.2% of the ferrous sulfate solution for foliar spray, spraying once every 5 to 7 days, continuous spraying 3 to 4 times; can also choose to use green leaf treasure, its The main ingredients are iron chelates and some trace elements. The spraying effect is better than simply spraying ferrous sulfate. Generally, 25 grams of water is used for 15 kilograms of mu and the spray is evenly sprayed. The spray is applied once every 10 days or so, continuous spraying. 2 to 3 times.
There are two types of dietary fibre - soluble and insoluble - and sweet corn contains both.
According to the American Heart Association, dietary fibre as part of an overall healthy diet can help lower blood cholesterol levels and may reduce the risk of heart disease. It is insoluble fibre that binds to cholesterol, preventing it from being absorbed into the bloodstream.
Insoluble fibre is responsible for promoting regularity and helping to prevent constipation by speeding up the passage of food and waste through the intestines and absorbing water to keep stools soft. Insoluble fibre has been shown to reduce the risk of haemorrhoids.
Fibre-containing foods such as sweetcorn also help to provide a sense of satiety and may therefore help to suppress appetite and aid weight management.
Dietary fibre has also been linked to a reduced risk of type 2 diabetes. A diet rich in fibre helps patients manage their disease.