[MCP 5.912] Proteomics Study of Clinical Dermatology - Psoriasis
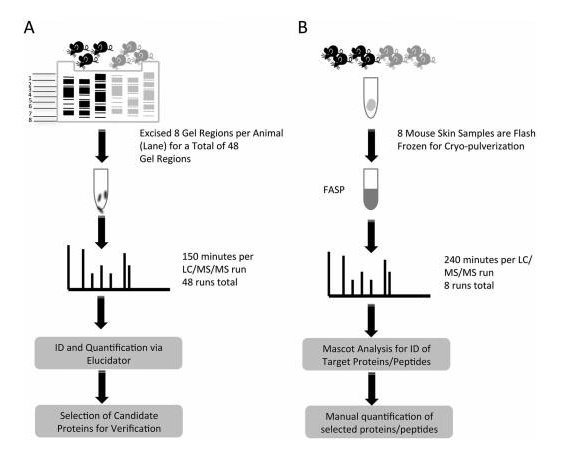
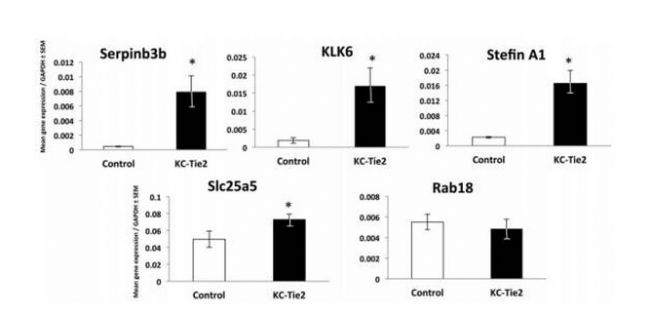
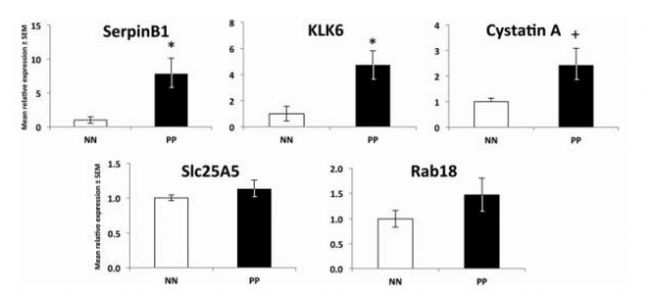
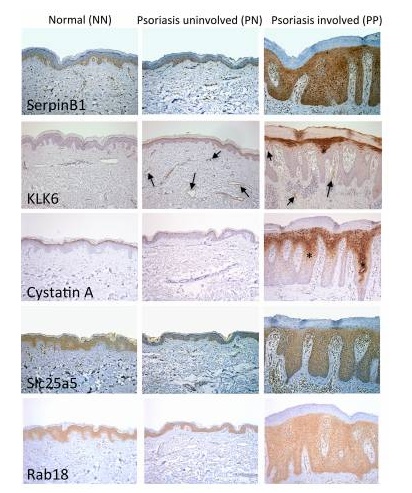
Proteomics of skin proteins in psoriasis: from discovery and verification in a mouse model to confirmation in humans. KC Lundberg, Y Fritz. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics, 2015, 14(1): 109-119 Source: https:// Background: Skin disease is a very common chronic disease. In particular, it is found that about 2-3% of people suffer from psoriasis, an immune-mediated inflammatory skin disease that brings extremes to patients' work and life. Big troubles. Studies have shown that psoriasis is associated with antigen-specific T lymphocytes, but the antigens involved are not known. Sample Source: KC-Tie2 Psoriasis Mouse Model Research Methods: Gel-Label free differential proteomics based on LC MS/MS Verification method: qPCR, LC-MS/MS-based Solution-Label-free (the same protein has two label-free results, the multiples are different, you can learn how to choose if you encounter this situation Result ) Research result: 1. Screen out the changes in proteome between model rats and normal mouse skin samples. Workflow summaries for the gel based label-free discovery and verification of target proteins approaches. 2. RT-PCR was used to detect several differentially expressed proteins at the mRNA level: Serpinb3b, KLK6, StefinA1, Slc25a5, Rab18, etc., and the difference was found to be significant. Candidate molecules identified from the gel-based label-free expression experiments are verified at the RNA level in control and KC-Tie2 mouse skin using qRT-PCR. 3. Confirmation of differential expression of several differential proteins using clinically psoriasis and normal human skin samples (not shown), including the initial keratinocytes (see figure below). Human psoriatic keratinocytes express higher levels of candidate gene transcripts compared with healthy control keratinocytes. Finally, the distribution of several differential proteins in tissues was detected by immunohistochemistry, and the existence of differences was further determined. Candidate proteins identified from gel-based label-free expression analyses of KC-Tie2 mouse skin are increased in lesional psoriasis patient skin. Xiaobian summary: This article is a very typical literature published in Molecular & Cellular Proteomics using the Proteomics Label free technology. In the DIscovery phase, the researchers first screened four proteins using the Gel-Labelfree differential proteomics method: stefin A1 (fold change 342.4), slc25a5 (fold change 46.2), serpinb3b (fold change 35.6), and kallikrein related peptidase 6 ( Fold change 4.7). In the Verification phase, verification methods one - qPCR, stefin A1 (fold change 7.3), slc25a5 (fold change 1.5), serpinb3b (fold change 17.4), and kallikrein related peptidase 6 (fold change 9). Verification Method 2 - Validation using the solution-Labelfree differential proteomics method, stefin A1 (fold change 29000), slc25a5 (fold change 1.3), and kallikrein related peptidase 6 (fold change 322). This method of using disease animal models in combination with differential proteomics is very efficient and meaningful for exploring disease mechanisms and screening for differential proteins as therapeutic targets. Protein|modification|metabolism|lipid|structural confirmation T: 021-54665263 E: Q: 1875681852 Urostomy Bag,Ileal Conduit Bag,Urostomy Bag Covers,Urine Ostomy Bag Wenzhou Celecare Medical Instruments Co.,Ltd , https://www.celecaremed.com