Rain in early summer to guard against watermelon blight
At the time of summer, the rapid temperature rise, coupled with a certain amount of recent rainfall, environmental conditions are conducive to the occurrence of watermelon blight, field blocks should be timely prevention and treatment. The watermelon blight is a fungal disease caused by the infection of watermelon-like bacillus, which mainly damages the vines and also damages the leaves and fruits. Melon vines at the beginning of the onset of the Department of oil-immersed faded cracks, and secrete rubber. When the disease is severe, the cracks on the vines burst, and the base of the main vines will also flow out of ash and red jelly; the side vines will crack and produce white oil. Some of the plants grew slowly or stopped growing; in severe cases, the whole plant died, and the vines became auburn after drying. Seedlings in the seedlings were damaged, and water spots began to appear in small spots, and then spread rapidly, causing the seedlings to die. The onset of leaf disease mostly starts from the leaf margin, producing "V"-shaped or semi-circular tan to large dark brown spots, with multiple bands. The onset of the fruit was initially a small, oil-like spot, followed by a dark-brown, round-shaped, submerged spot. The surface was cracked star-shaped, followed by dense black spots. The watermelon sprain does not harm the roots and vascular bundles, and a large number of small black spots and amber-like granules are produced on the lesions, which can be distinguished from anthracnose, blight, and disease. The bacterial pathogens of the blight are overwintering on the soil and in the frame with mycelium, conidiospores and ascendants. Unpredictable weather conditions, especially under conditions of high temperature and high humidity, make the disease easily prevalent. In addition, diseases such as melon crops, cultivation of greenhouses and greenhouses, low-lying areas, lush crops, poor ventilation, high humidity, and weak crop conditions are serious. To prevent watermelon blight, pay attention to balanced fertilization and open a good "three ditch" to facilitate drainage and dehydration. For the already affected fields, 95% virulent WP can be used alternately 3000 times; or 64% virulent Mn-Zn wettable powder 500 times; or 70% thiophanate-methyl wettable powder (1000%) Diluent) plus Fuxing 40% fluorosilicone EC (10000 times liquid); or 50% isoprenil wettable powder 1500 times spray control, 5 to 7 days once, continuous control 3 to 4 times. In order to avoid affecting pollination, the watermelon should be applied after the initial flowering after 4pm. For a small number of diseased plants that can also be combined with smears, treat 2 parts of 50% carbendazim WP 1 part of 15% triadimefon wettable powder (not emulsifiable concentrate), mix with water and dilute into a thin paste, apply with a brush. Stem, lesions of diseased plants (first cut off the lesions with a knife). In addition, the sick field should pay attention to control watering, timely clear the sick and concentrate to destroy.
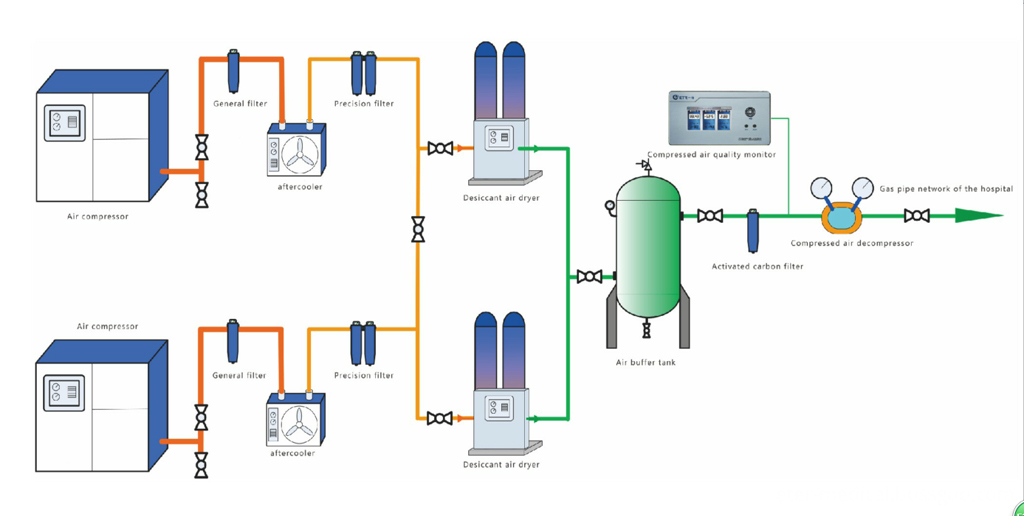
The
medical compressed air plant consists of the air compressor, general
filter, aftercooler, precision filter, desiccant air dryer, air buffer
tank, activated carbon filter, compressed air quality monitor,
decompressor, valve, pipeline and terminal. The system generates
compressed air through an air compressor, removes the impurities, oil
mist and moisture in the compressed air through an adsorption dryer
filter unit, delivers the air to the air storage tank and supplies it
through a pipeline to the terminal equipment in the operating room, ICU
and other inpatient wards after decompression.
Medical Compressed Air Plant Medical Compressed Air Plant ,Hospital Gas System ,Hospital Gas Pipeline System ,Medical Air Compressor Hunan Eter Electronic Medical Project Stock Co., Ltd. , https://www.centralgas.be