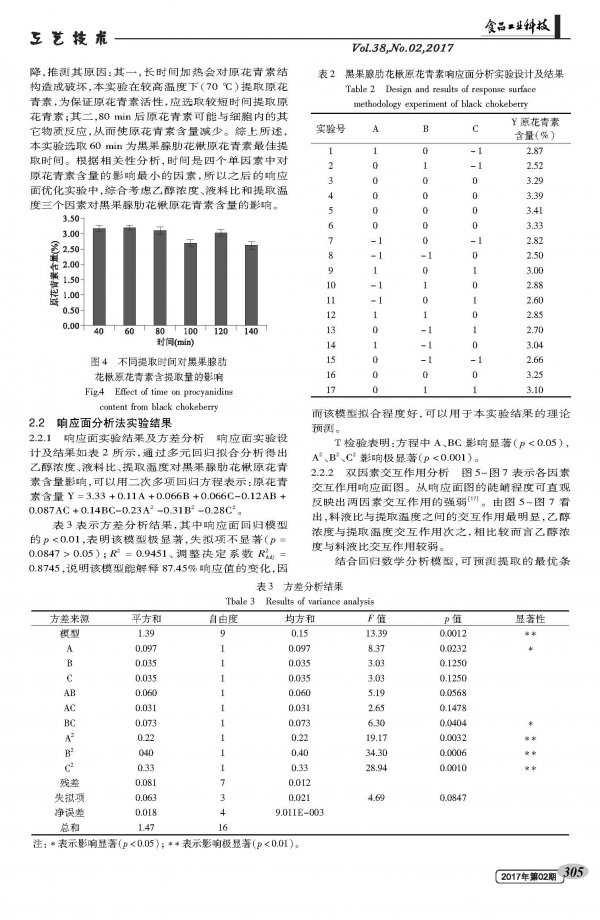
Extraction and Antibacterial Activity of Proanthocyanidins from Black Fruit Gland
Black fruit gland ribs, also known as wild cherry, not old berries, Rosaceae, native to the northeastern United States. The fruit tree is an economic forest tree species mainly producing fruits. The fruit has high nutritional value and medicinal value. It is a precious tree species that combines edible, medicinal, landscaping and ecological protection. Since the early 1990s, the Afforestation Research Institute of the Arid Region of Liaoning Province has begun the experimental research on the introduction, cultivation and fruit processing and utilization of the Chinese genus. The fruit of the black fruit gland has a variety of nutrients, such as dietary fiber, sugar, protein, polyphenols, etc., the most important of which is phenolic substances. Phenolic substances such as phenolic acid, proanthocyanidins, anthocyanins, flavonols, etc. are abundant and closely related to the biological activity of the black fruit gland. The polyphenols in the fruit of the black fruit gland are mainly divided into monomeric polyphenols and polymeric polyphenols. The monomeric polyphenols are mainly phenolic acids, flavonoids and their terpenoids, anthocyanins and their glycosides; polymeric polyphenols are proanthocyanidins. The proanthocyanidins in the fruit of the black fruit gland were 41.9%~59.1% of the total phenols. The content of proanthocyanidins in the phenolic substances of the black fruit gland was the highest, which was crucial for the biological activity of the black fruit gland. The role. Proanthocyanidins have anti-oxidative activity, anti-cardiovascular disease, anti-cancer, anti-hypertension, blood sugar lowering and other biological activities; their antioxidant capacity is 50 times that of Ve and 20 times of Vc, which is the best natural antioxidant found so far. First, the antibacterial and antiviral effects of proanthocyanidins have been studied for nearly 30 years. Studies have shown that certain concentrations of proanthocyanidin solution have inhibitory effects against Rhizoctonia solani, Fusarium oxysporum and Helminthosporium megacephala. At present, proanthocyanidins have been widely used in medicine, health care products and food. The extraction methods of proanthocyanidins include ultrasonic method, organic solvent extraction method and microwave method. In this paper, the extraction process of proanthocyanidins was studied by using ultrasonic-assisted extraction method, and the response process surface analysis method was used to optimize the extraction process parameters, and the antibacterial activity of the anthocyanins of the black fruit gland. Conduct research to provide a scientific basis for the in-depth development and comprehensive utilization of the proanthocyanidins of the black fruit gland.