Types and causes of failure of piston refrigeration compressor
Germany imported beads
Imported French lens
mould Die-casting Eight edge type Revolving arm
Optional emergency power supply≥3 hours
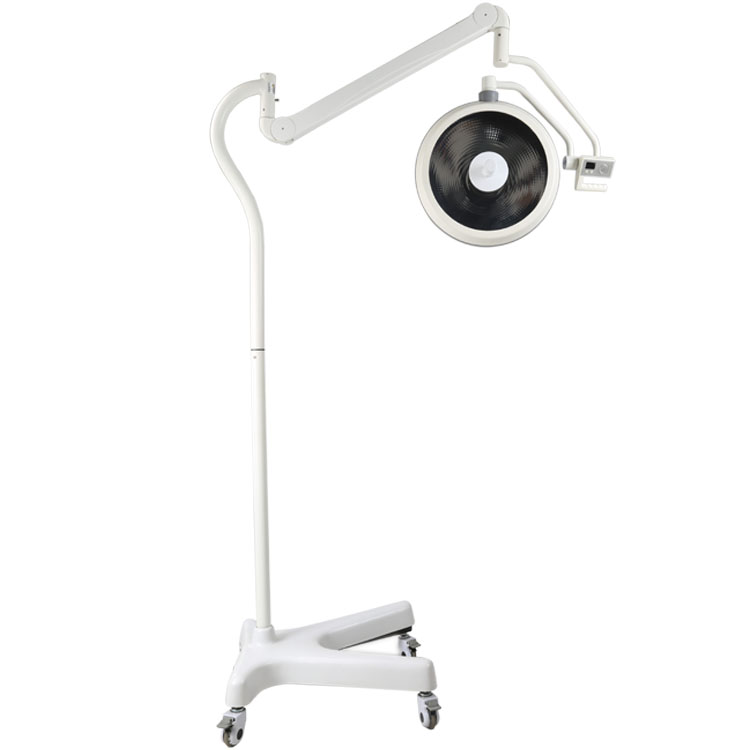
Main Feature:
1.ZF series of reflective shadowless lamp is widely used in various occasions operation lighting needs,is the ideal lighting equipment of modern operation room.
2.Full close streamline lamp body design completely meets the demand of the sterilization and high standard of laminar flow purification in operation room.
3.Adopting more than 5280 slices of reflection mirror, guaranteeing 1200 mm lighting depth.
4.Special design of color temperature compensation provides closer to that of natural sunlight and helps the doctor to distribute operation parts clearly and accurately.
5.The back-up bulb will start work within 0.2 seconds automatically in case the main bulb is damaged,ensuring the continuation of surgical operation. There`s failure indication in the handle control panel,to recommend the bulb to be changed after operation.
6.Detachable handle jacket ,can be used for high temperature (≤134℃)sterilized.
7.Digital-control circuit offers many functions, with 10 segment brightness selection stepless lighting regulation,brightness memory, low voltage start-up and power on self test etc.
8.The life-span of OSRAM halogen bulb is up to 1500 hours; the bulbs can be changed easily.
9.Germany ORSAM lamp socket,thermostability
10.Balance arm can be optional Germany imported or domestic.
11.Mould Die-casting Eight edge type Revolving arm
Overall Reflex LED Operating Light Overall Reflex LED Operating Light,LED Surgical Lights,Overall Reflex LED Operating Light,Reflection Operating LED Light Shandong Kang'erjian Medical Technology Ltd. , https://www.operatingtable.nl
The following is a simple classification of common compressor failures:
l, the compressor can not start normally
(1) The power supply voltage is too low; the motor line is in poor contact;
(2) The exhaust valve plate leaks. Cause the pressure inside the crankcase to be too high;
(3) The energy regulation mechanism fails;
(4) The temperature controller is out of adjustment or malfunctions;
(5) The pressure relay is out of order.
2. The compressor starts and stops frequently:
(1) Due to the leakage of steam from the exhaust valve, the pressure in the high and low parts is balanced, causing the inlet pressure to be too high;
(2) The temperature relay amplitude difference is too small;
(3) The high voltage relay operates due to excessive pressure caused by the lack of water in the condenser.
3. There is no oil pressure after the compressor starts or the oil pressure does not work during operation:
(1) Oil leakage or pipeline blockage at the connection of the oil pump piping system;
(2) The oil pressure regulating valve is opened too much or the spool is detached;
(3) too little crankcase oil;
(4) There is ammonia in the crankcase, and the oil pump does not enter the oil;
(5) The oil pump is seriously damaged and the clearance is too large;
(6) The connecting rod bearing bush and the crank pin, the connecting rod small head bushing and the piston pin are seriously damaged;
(7) The oil pressure gauge valve is not open.
4, the oil pressure is too high
(1) The oil pressure regulating valve is not opened or opened too small;
(2) Internal blockage of the oil circuit system;
(3) The oil pressure regulating valve spool is stuck.
5, the oil pump does not press
(1) The oil pump parts are seriously damaged, resulting in excessive clearance;
(2) The oil pressure gauge is not allowed, and the pointer is out of order;
(3) Improper assembly of the oil pump components after inspection.
6. The lubricating oil in the crankcase foams
(1) A large amount of ammonia liquid is mixed in the lubricating oil, and the foam is caused by evaporation of the ammonia liquid when the pressure is lowered;
(2) The crankcase is too much oiled, and the connecting rod is attracted by the lubricating oil.
7, the oil temperature is too high
(1) There is no water supply to the crankcase oil cooler;
(2) The shaft and tile are not properly assembled, and the clearance is too small;
(3) The lubricating oil contains impurities, causing the bearing bush to pull;
(4) The shaft seal friction ring is installed too tightly or the friction ring is pulled;
(5) The temperature of suction and exhaust steam is too high.
8, oil pressure instability
(1) The oil pump draws in foamed oil;
(2) The oil circuit is not smooth.
9, the compressor consumes too much fuel
(1) The oil ring is seriously damaged and the assembly clearance is too large;
(2) The oil ring is reversed, and the lock of the ring is installed on a vertical line;
(3) The gap between the piston and the cylinder is too large;
(4) The exhaust steam temperature is too high, so that the lubricating oil is carried away by the airflow;
(5) The crankcase oil level is too high;
(6) The automatic oil return valve of the oil separator is not working, and the oil cannot be automatically returned to the crankcase and discharged.
10. Crankcase pressure rises
(1) The piston ring is not tightly sealed, causing high pressure to low pressure;
(2) The exhaust valve is not closed tightly;
(3) The cylinder liner and the sealing surface of the machine body leak;
(4) The ammonia solution enters the crankcase and evaporates to cause the pressure to rise.
11, the energy regulation mechanism is malfunctioning
(1) The oil pressure is too low;
(2) the tubing is blocked;
(3) oil piston pipe;
(4) The tie rod and the rotating ring are not installed correctly, and the rotating ring is stuck;
(5) The oil distribution valve is improperly assembled.
12, the exhaust steam temperature is too high
(1) The condensing pressure is too high;
(2) The return steam pressure is too low;
(3) The steam is overheated;
(4) The clearance at the top dead center of the piston is too large;
(5) The cylinder head cooling water is insufficient.
13, the steam superheat is too high
(1) The ammonia solution in the evaporator is too small, and the liquid supply valve is small;
(2) The insulation of the steam return pipe is poor or the insulation layer is damaged by moisture;
(3) The suction valve piece leaks or ruptures.
14, the exhaust steam temperature is too low
(1) compressor wet stroke;
(2) The intercooler supplies too much liquid.
15. Compressor suction pressure is lower than normal evaporation pressure
(1) The liquid supply valve is too small to open, and the liquid supply is insufficient, so the evaporation pressure is lowered;
(2) The valve in the suction line is not fully open;
(3) The valve core of the valve in the suction pipe is detached;
(4) The amount of liquid ammonia in the system is insufficient. Although the liquid supply valve is opened, the pressure does not rise;
(5) The suction filter is clogged;
(6) There is a “sac†phenomenon in the steam return line;
(7) The return pipe is too thin.
16, the pressure gauge pointer beats violently
(1) There is air in the system;
(2) The pressure gauge pointer is loose;
(3) The valve opening is too large;
17. Compressor exhaust pressure is higher than condensing pressure
(1) The valve in the exhaust pipe is not fully open;
(2) partial blockage in the exhaust pipe;
(3) The design of the exhaust pipe is unreasonable.
18, compressor wet stroke
(1) The liquid supply valve is opened too large;
(2) The suction shut-off valve is opened too fast at startup;
(3) When the cold storage tank is restored to normal cooling, the suction shut-off valve opens too fast;
19. There is a knocking sound in the cylinder.
(1) The clearance at the top dead center of the piston is too small;
(2) The clearance between the piston pin and the small hole of the connecting rod is too large;
(3) The suction and exhaust valve pieces are loosened;
(4) The false cover spring is deformed and the elastic force is reduced;
(5) The clearance between the piston and the cylinder is too large;
(6) The lubricating oil is too much or not clean;
(7) the valve piece breaks into the cylinder;
(8) Liquid ammonia is flushed into the cylinder to produce a liquid hammer.
20, the crankcase has a knocking sound
(1) The gap between the connecting rod big head tile and the crank pin is too large;
(2) The main bearing and the main journal are too large;
(3) The split pin is broken and the connecting rod nut is loose.
21, cylinder pull hair
(1) The size of the gap between the piston and the cylinder, and the size of the piston ring pin is incorrect;
(2) The vapor contains impurities;
(3) The viscosity of the lubricating oil is too low or has impurities;
(4) The exhaust steam temperature is too high, causing the viscosity of the oil to decrease.
22, shaft seal oil leakage is serious
(1) Poor assembly;
(2) pulling the friction surface of the moving ring and the fixing ring;
(3) The rubber school seal ring is not suitable for aging or tightness;
(4) The shaft seal spring force is weakened;
(5) The back of the fixing ring is not sealed with the shaft sealing gland;
(6) The crankcase pressure is too high.
23, shaft seal oil temperature is too high
(1) insufficient lubricant;
(2) The lubricating oil is not clean;
(3) The friction surface pressure between the moving ring and the fixed ring is too tight;
(4) The main bearing assembly clearance is too small.
24, the piston stuck in the cylinder
(1) The lubricating oil is inferior and has many impurities;
(2) The cylinder is short of oil;
(3) The cylinder temperature changes drastically;
(4) The clearance of the piston ring is too small.